When you hear cloud computing, what comes to your mind? It’s quite vast, and in simple terms, cloud computing is the delivery of different computing services through the internet. These computing services can include databases, analytics, storage, and machine learning, among many other things. As a cloud solutions provider, we’ve seen them all and can help make common sense of cloud computing.
Below is a quick guide to the four types of cloud computing and their use cases.
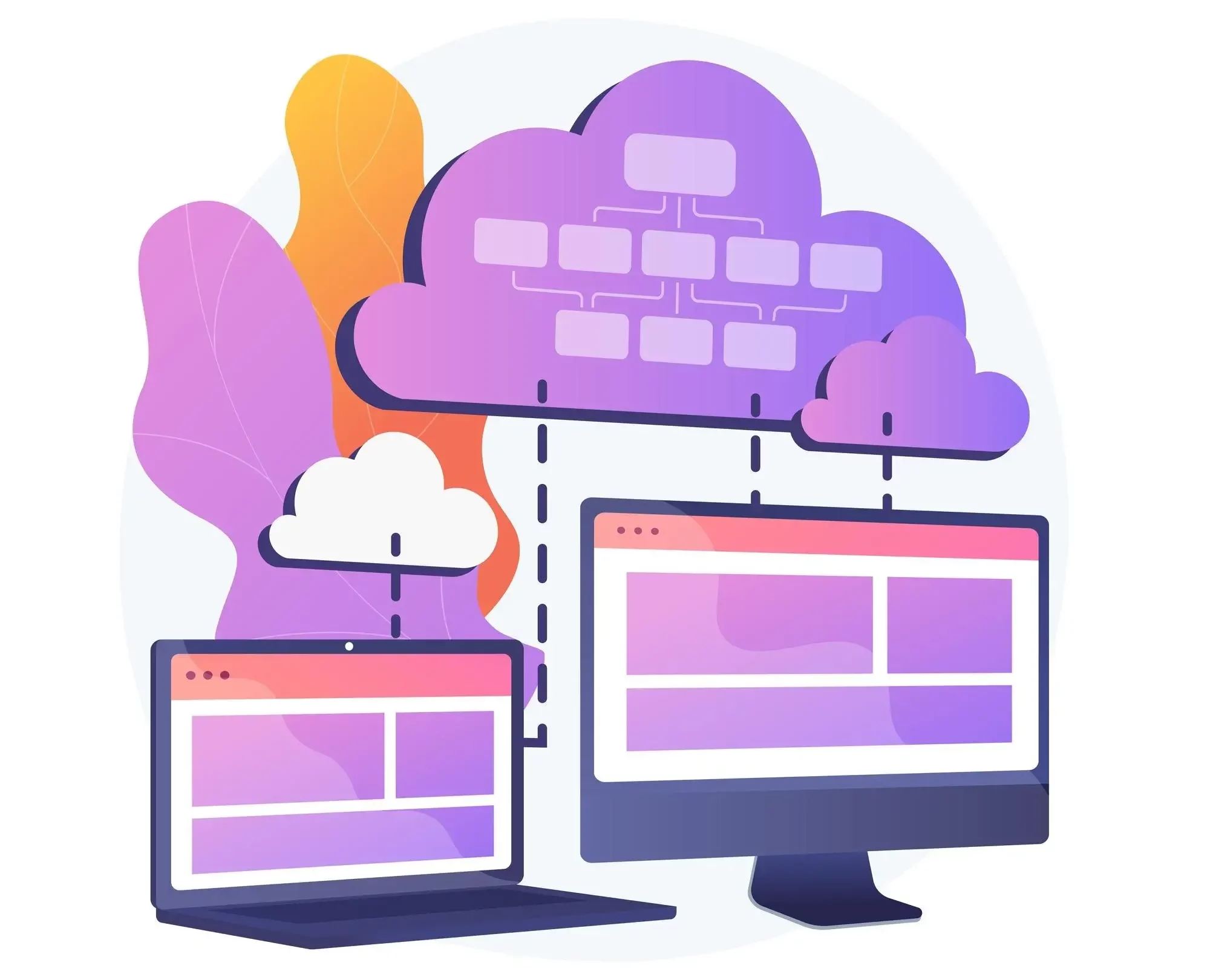
The Four Types Of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is divided into four main types: public clouds, private clouds, hybrid clouds, and multi-clouds. Caution must be taken when choosing a cloud type because switching costs are usually a Herculean lift that comes with a big price tag. Additionally, each cloud type is designed for different use cases, and even if two clouds are of the same type, they’ll likely still be configured differently.
1. Public Clouds
Public clouds are what most of us think of first, and are virtual resources built on hardware. It is owned and managed by cloud service providers and is automatically allocated or shared amongst multiple tenants through the internet. Management, resource allocation, and user agreements are the unique features that make this cloud public. Some of the most popular and largest public cloud providers include Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services ( AWS), IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. Many startups and new products use public clouds to easily scale their technology and serve static assets, such as websites and content.
2. Private Clouds
Private clouds reside within a company’s own infrastructure. The difference between private and public clouds is that, with private clouds, the company bears the burden of infrastructure maintenance and security. Additionally, while public clouds can be shared by multiple tenants, private clouds often stay restricted to a single organization. If you’re from a large enterprise, think of your company intranet. And even though a private cloud is harder to set up and maintain, larger organizations often use private clouds to comply with data and privacy laws, such as KYC and HIPAA. Private clouds also provide granular monitoring that can protect against intellectual property leaks and theft.
3. Hybrid Clouds
Hybrid clouds combine both public and private clouds. Hybrid clouds incorporate management, portability, and orchestration across two or more organizations or departments within the organization. These environments may have two or more private clouds, two or more public clouds, one private and one public cloud, or a virtual environment with at least one private or public cloud. Even in highly regulated industries like law and healthcare, hybrid clouds are used: a public cloud for non-sensitive data, such as a website, and a private cloud for sensitive data, such as an EMR.
4. Multi-Clouds
Multi-clouds are cloud services that use more than one cloud service or cloud service provider, public or private. Multi-cloud environments reduce reliance on a single cloud service provider by distributing software, cloud assets, applications, and more across multiple providers. Multi-clouds de-risk your organization and can help determine a preferred cloud vendor. For instance, your organization may host your website on Azure and have a failsafe version on AWS. The same can be done for core business services, such as health testing applications.
The Bottom Line
Cloud computing has repeatedly proven important for numerous reasons, including flexibility, data recovery, increased security, automatic software updates, and easy access. So if your organization isn’t already in the cloud or is considering it, contact us today for a free consultation to determine whether public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud is the right solution for you!
We can also audit your cloud infrastructure to identify opportunities for performance and cost optimizations!